
In today’s complex and rapidly changing world, innovation is no longer a buzzword—it’s a fundamental necessity for organizations that want to remain relevant, competitive, and impactful. At its core, innovation is the process of turning ideas into tangible value. It can take the form of new products, services, processes, technologies, or business models, but always with the aim of generating measurable improvement.
Whether you’re aiming to solve unmet customer needs, drive sustainability, or seize new market opportunities, innovation offers the tools to rethink, reframe, and redesign how your organization operates.
What Is Innovation?
Innovation refers to the process of transforming creative ideas into effective solutions that generate value. This could mean launching a new product, reengineering a process, designing a better user experience, or redefining how your business model works.
It involves more than just invention—it’s about execution, impact, and scalability. Innovation can be incremental or disruptive, internal or open, but it always challenges the status quo and encourages experimentation, learning, and adaptation.
The Foundations of Innovation
Effective innovation doesn’t happen by chance. It’s enabled by a set of interconnected factors:
- Creative Thinking
Innovation starts with ideas—whether small improvements or bold reinventions. Creativity allows teams to make connections, see new possibilities, and challenge assumptions. - Organizational Culture
A true culture of innovation encourages risk-taking, collaboration, learning from failure, and openness to change. When teams feel empowered to explore, innovation flourishes. - Leadership and Strategic Vision
Innovation requires leadership that sets direction, removes barriers, and models curiosity. Visionary leaders prioritize experimentation and align innovation with business goals. - Resources and Infrastructure
Innovation needs the right support—funding, time, talent, technology, and tools. Investing in innovation capabilities shows long-term commitment. - Feedback Loops
Continuous feedback from customers, users, and partners ensures innovation stays grounded in real needs. Feedback enables iteration and improvement. - Risk Management
All innovation involves uncertainty. Effective organizations balance bold action with the ability to evaluate, manage, and mitigate risks at each stage.
Types of Innovation
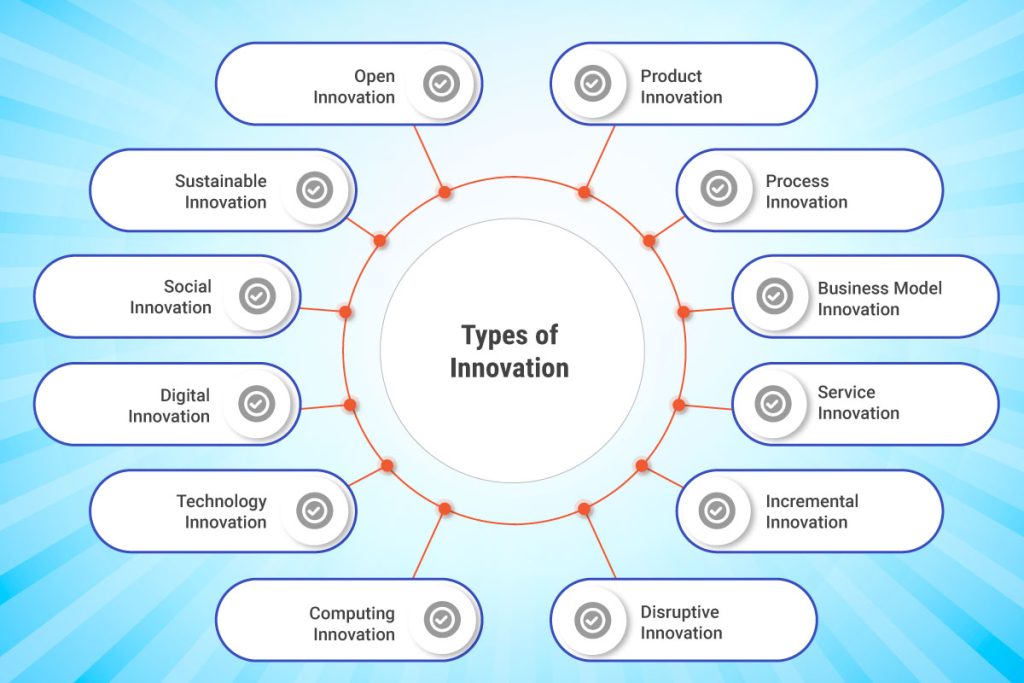
Innovation can take many forms depending on the challenge or opportunity at hand. Here are some of the most relevant types:
- Product Innovation: Creating or improving products to meet new needs or enhance performance.
- Process Innovation: Optimizing how things are done—improving efficiency, reducing costs, or enhancing quality.
- Business Model Innovation: Redefining how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value.
- Service Innovation: Improving customer experiences through new or better service delivery methods.
- Incremental Innovation: Making small but meaningful improvements to existing products or systems.
- Disruptive Innovation: Introducing radically new solutions that redefine markets or displace incumbents.
- Open Innovation: Co-creating with customers, partners, startups, or universities to accelerate discovery and development.
- Sustainable Innovation: Designing solutions that reduce environmental impact and promote long-term responsibility.
- Social Innovation: Tackling social issues with new models that promote equity, inclusion, and wellbeing.
- Digital and Technological Innovation: Leveraging emerging technologies (AI, IoT, blockchain, etc.) to drive transformation.
Organizations may also approach innovation as:
- Continuous (evolutionary improvement), or
- Discontinuous (radical breakthroughs that reset the playing field).
Each type contributes differently to competitive advantage and long-term growth.
Innovation in Action: Transformational Examples
Real-world innovations that have reshaped industries include:
- Airbnb: Redefined travel with a peer-to-peer model that empowered individuals to monetize unused space.
- Tesla: Made electric vehicles aspirational, scalable, and a symbol of clean mobility.
- SpaceX: Revolutionized space travel with reusable rockets, slashing costs and timelines.
- Netflix: Moved from DVD rentals to a personalized, on-demand streaming platform.
- CRISPR: Enabled gene editing with unprecedented accuracy—reshaping medicine and agriculture.
- 3D Printing: Made on-demand, customized manufacturing accessible across sectors.
- Mobile Payment Systems: Apple Pay and Google Pay redefined convenience in daily transactions.
- Amazon Alexa: Introduced voice as a mainstream user interface, transforming human-machine interaction.
- Micromobility: E-scooters and bike-sharing changed urban transport habits and reduced emissions.
- Solar Tech: Innovations in panels and battery storage brought renewable energy into everyday homes.
These examples show how innovation can come from redefining convenience, lowering barriers, or solving persistent challenges—and how it can reshape entire ecosystems.
The Innovation Process: From Idea to Execution
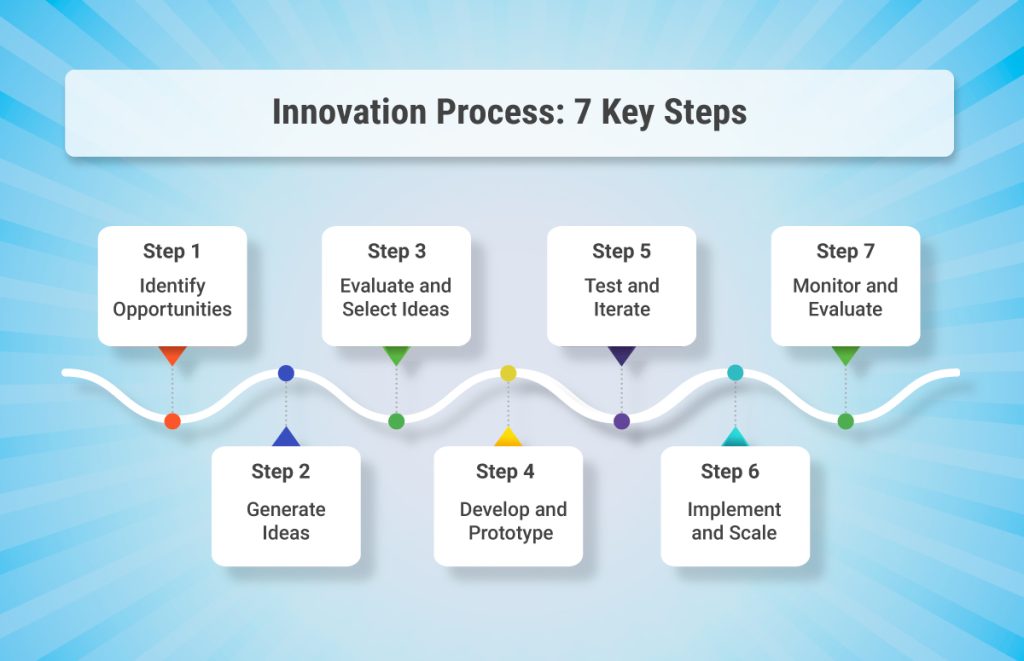
Innovation is not a one-off event—it’s a structured journey. The following steps form a reliable roadmap:
- Opportunity Identification
Spot unmet needs, emerging trends, or internal inefficiencies through research and analysis. - Ideation
Generate a broad range of ideas via workshops, customer co-creation, or cross-functional collaboration. - Evaluation and Selection
Prioritize ideas based on feasibility, desirability, market potential, and strategic alignment. - Concept Development
Translate ideas into prototypes or MVPs. Test assumptions early and gather user feedback. - Iteration and Testing
Refine solutions through real-world testing and agile sprints. Learn quickly and adjust. - Implementation and Scaling
Develop go-to-market strategies, align resources, and bring innovations to life at scale. - Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Measure outcomes, gather insights, and adapt to changing conditions. Innovation should evolve with your business.
This process should be cyclical—an engine of continuous learning and renewal.
Final Thoughts: Innovation as a Strategic Imperative
Innovation is not reserved for tech giants or R&D labs. It is a mindset, a capability, and a strategic advantage available to every organization willing to embrace change, invest in creativity, and challenge traditional thinking.
At ICD, we support organizations in designing and executing innovation strategies tailored to their context. Whether you’re looking to innovate your business model, build a culture of innovation, run a product ideation sprint, or implement a scalable innovation framework, we help you turn ideas into real outcomes.
👉 Let’s explore how innovation can drive your transformation. Contact us today.
