In today’s fast-moving business environment, innovation can no longer be confined within company walls. The most transformative breakthroughs often come from collaboration, knowledge exchange, and strategic partnerships. This is the essence of open innovation—an approach that actively seeks ideas, technologies, and expertise from both internal and external sources to accelerate growth and deliver value faster.
Open innovation recognizes a simple truth: great ideas can emerge anywhere—inside the organization, from customers, startups, research institutions, or even competitors. The companies that know how to identify, integrate, and scale these ideas are the ones that consistently lead their industries.
What Is Open Innovation?
Open innovation is a structured approach to innovation that embraces external collaboration alongside internal R&D. Unlike the traditional “closed” model—where innovation is developed solely in-house—open innovation invites contributions from outside the organization to complement internal capabilities.
This collaborative model connects companies to a broader network of expertise, allowing them to develop, test, and commercialize solutions faster and more efficiently.
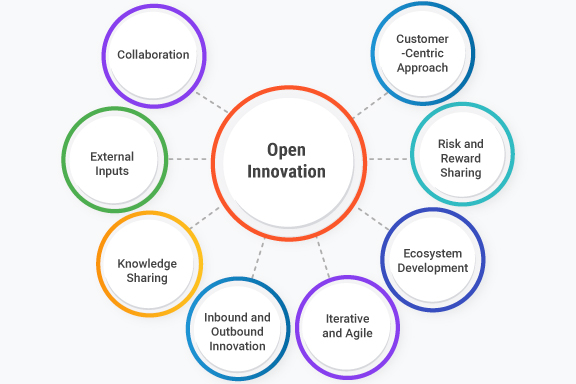
Key Features of the Open Innovation Model
The open innovation model stands out for several defining characteristics:
- Collaboration Across Boundaries
Partnerships with customers, suppliers, universities, startups, and even competitors expand the scope of potential ideas. - External Knowledge Inputs
External insights, technologies, and solutions complement internal R&D, accelerating development cycles. - Knowledge Sharing
Exchange of expertise and resources through networks, platforms, and partnerships promotes mutual growth. - Inbound & Outbound Innovation
Inbound innovation brings external ideas into the organization.
Outbound innovation commercializes internal ideas through licensing, partnerships, or joint ventures. - Ecosystem Building
Innovation thrives in connected ecosystems—incubators, accelerators, clusters, and co-creation platforms. - Shared Risk & Reward
Collaborative models distribute both investment and returns among multiple stakeholders. - Customer-Centric Focus
Customers actively shape solutions through feedback, co-creation, and early-stage testing.
Benefits and Challenges of Open Innovation
Open innovation offers powerful advantages—but also requires careful management.
Advantages
- Access to a wider pool of ideas and expertise.
- Faster time-to-market by leveraging external capabilities.
- Reduced R&D costs through shared resources.
- Greater agility in responding to market shifts.
- Enhanced competitiveness via diverse perspectives.
Challenges
- Intellectual property protection and ownership.
- Managing large volumes of external ideas effectively.
- Coordinating multiple partnerships and expectations.
- Ensuring quality and alignment of external contributions.
- Overcoming cultural barriers and internal resistance to openness.
Types of Open Innovation Models
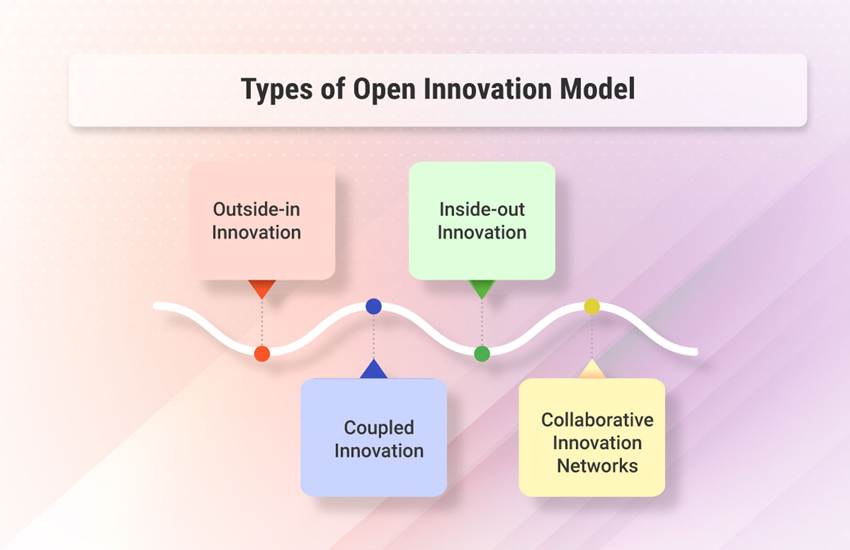
Open innovation can take different forms, often combined for maximum impact:
- Outside-In Innovation
Bringing external ideas, technologies, or insights into the organization (e.g., customer idea platforms, startup partnerships). - Inside-Out Innovation
Licensing or commercializing internal ideas externally (e.g., patents, technology licensing, spin-offs). - Coupled Innovation
Co-developing solutions through joint ventures, alliances, or customer co-creation projects. - Collaborative Networks
Innovation ecosystems or online platforms that connect multiple stakeholders to co-create and share solutions.
Real-World Examples of Open Innovation
- LEGO – The LEGO Ideas platform turns fan designs into official products, tapping into community creativity.
- NASA – Global competitions and patent licensing open the space agency’s challenges to external solvers.
- Procter & Gamble – Connect + Develop sources innovations from startups, inventors, and suppliers.
- IBM – The IBM Q Network collaborates with universities and partners to advance quantum computing.
- Mozilla – Open contributions from developers shape the Firefox browser and new digital tools.
- GE Appliances – FirstBuild engages engineers, makers, and consumers in co-developing appliances.
Best Practices for Implementing Open Innovation
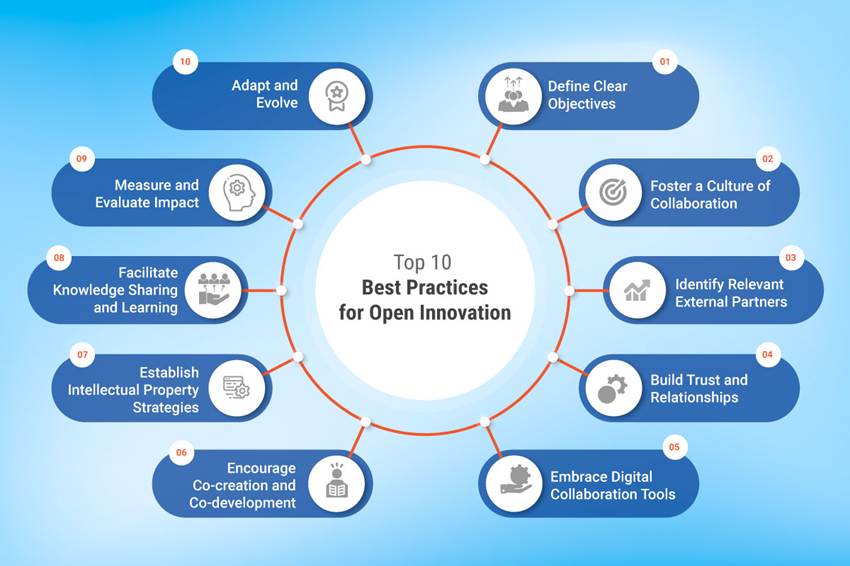
To successfully adopt open innovation, organizations should:
- Set Clear Objectives – Define the innovation challenge, desired outcomes, and value expectations.
- Promote a Collaborative Culture – Internally encourage openness, knowledge sharing, and partnership.
- Engage in Co-Creation – Work closely with customers, suppliers, and partners to co-develop solutions.
- Select the Right Partners – Identify partners that align in vision, expertise, and capabilities.
- Build Trust – Establish transparency and clear expectations from the start.
- Facilitate Knowledge Exchange – Share insights, success stories, and lessons learned across the organization.
- Leverage Digital Tools – Use platforms for idea submission, project management, and collaboration.
- Protect Intellectual Property – Put IP frameworks in place to manage rights and ownership.
- Measure Results – Track the impact of open innovation in terms of revenue, speed, and market reach.
- Adapt Continuously – Stay flexible and ready to evolve strategies as technologies and markets change.
At ICD, We Help You Build Powerful Innovation Ecosystems
Open innovation is more than a methodology—it’s a mindset and a capability. At ICD, we work with organizations to design, implement, and manage open innovation frameworks that connect them with the right partners, platforms, and ecosystems. From co-creation initiatives and startup collaborations to innovation challenges and IP strategy, we help organizations tap into the power of collective intelligence.
Let’s explore how open innovation can accelerate your growth. Contact us today.
